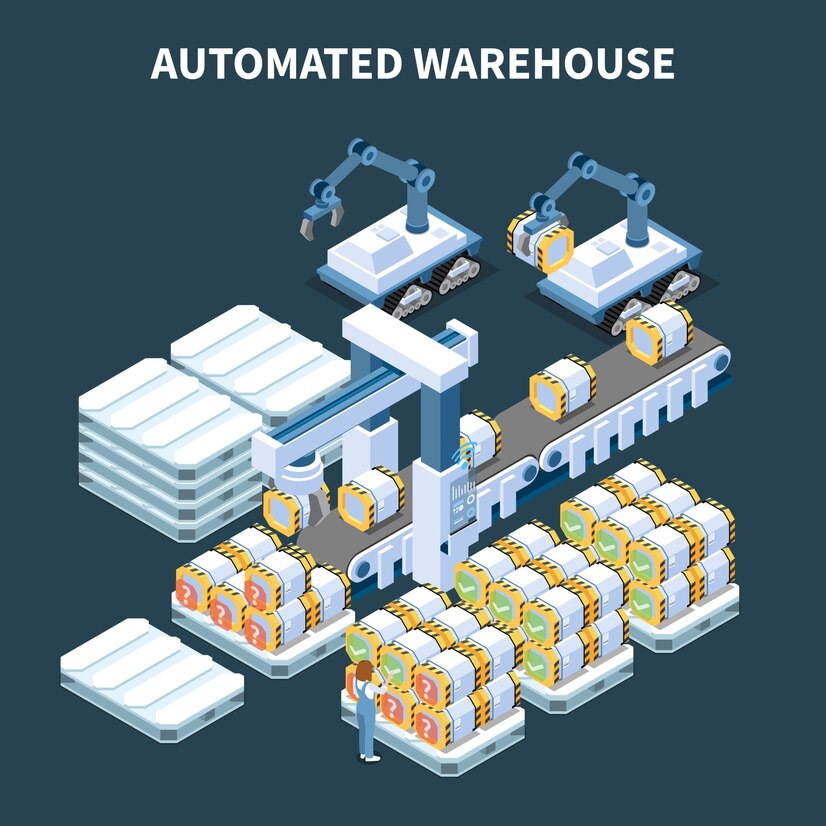
In the era of Industry 4.0, the concept of the automated warehouse has become a cornerstone for businesses aiming to enhance efficiency, reduce operational costs, and stay competitive in an ever-evolving market. Automation in warehousing involves using technology to streamline operations, including inventory management, picking processes, and material handling. This article delves into the significance of automated warehouses, the technologies driving this revolution, and how companies leverage these innovations to optimize their supply chains.
The Need for Automation in Warehousing
Traditional warehousing methods struggle to keep pace as consumer expectations shift towards faster delivery times and increased order accuracy. Manual processes are labor-intensive, time-consuming, and prone to errors, leading to customer dissatisfaction and increased costs. Implementing an automated warehouse addresses these challenges by:
- Enhancing Efficiency: Automation reduces the time taken for tasks such as picking, packing, and shipping, thereby increasing throughput.
- Improving Accuracy: Automated systems minimize human errors in inventory management and order fulfillment.
- Optimizing Space Utilization: Advanced storage systems maximize the use of warehouse space, allowing for higher storage density.
- Reducing Labor Costs: Automation decreases reliance on manual labor, mitigating the impact of labor shortages and reducing staffing expenses.
- Boosting Safety: Automated equipment can handle hazardous tasks, reducing the risk of workplace injuries.
Key Technologies in Automated Warehouses
- Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (ASRS)
ASRS are computer-controlled systems that automatically place and retrieve loads from defined storage locations. These systems include mini-loaders, shuttle systems, and crane-based storage solutions, enhancing speed and accuracy in handling goods. - Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMRs)
AMRs navigate warehouse floors using sensors and maps to transport materials without human intervention. They are flexible and can adapt to changes in the warehouse layout, making them ideal for dynamic environments. - Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs)
AGVs are driverless vehicles that follow predefined paths using magnetic strips, wires, or sensors. They are used for repetitive tasks like transporting goods over long distances within the warehouse. - Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
Advanced WMS software integrates with automated equipment to provide real-time data on inventory levels, order status, and equipment performance. This integration enables better decision-making and efficient resource allocation. - Robotic Picking Systems
Robotic arms equipped with advanced grippers and vision systems can pick and place items quickly. This technology reduces errors in order fulfillment and increases the speed of the picking process.
Leading Providers of Automated Warehouse Solutions
PHS Innovate
PHS Innovate is a provider of automated material handling solutions, offering customized systems tailored to the specific needs of businesses in Australia and New Zealand. Their expertise includes:
- Automated Warehousing Solutions: Implementing ASRS and WMS to optimize storage and retrieval processes.
- Autonomous Mobile Robots: Deploying AMRs to enhance flexibility and productivity in material transport.
- Pallet Handling Systems: Providing advanced pallet storage, retrieval, and transportation solutions.
SSI SCHAEFER
SSI SCHAEFER is another key player in the field of warehouse automation. With a global presence, they offer a wide range of solutions:
- Warehouse Automation Systems: Customized automation solutions to increase efficiency and productivity.
- Automated Guided Vehicles: Advanced AGVs designed to move materials safely and efficiently within facilities.
- Robotic Systems: Innovative robotic applications for picking, packing, and palletizing.
Benefits of Implementing an Automated Warehouse
- Scalability
Automated systems can be scaled up or down based on business needs, allowing companies to adapt to market demands without significant overhauls. - Data-Driven Insights
Automation provides access to real-time data analytics, enabling businesses to identify trends, forecast demand, and optimize operations. - Enhanced Customer Satisfaction
Faster order processing and accurate deliveries lead to improved customer experiences, fostering loyalty and a positive brand reputation. - Environmental Sustainability
Efficient operations reduce energy consumption and waste, contributing to environmental sustainability goals.
Challenges and Considerations
While the advantages are significant, companies must consider the following when transitioning to an automated warehouse:
- Initial Investment: The upfront costs for equipment and software can be substantial.
- Integration Complexity: Ensuring new systems integrate seamlessly with existing processes and technologies.
- Workforce Impact: Retraining staff to work alongside automated systems and addressing potential job displacement concerns.
Future Trends in Warehouse Automation
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning: AI-driven systems will enhance decision-making and predictive maintenance.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Increased connectivity between devices for real-time monitoring and control.
- Collaborative Robots (Cobots): Robots working alongside humans to enhance flexibility and efficiency.
Conclusion
The rise of the automated warehouse marks a significant shift in how businesses manage their supply chains. By embracing automation, companies can achieve greater efficiency, accuracy, and adaptability in their operations. Providers like PHS Innovate and SSI SCHAEFER are at the forefront of delivering innovative solutions that meet the evolving needs of the industry.
Investing in warehouse automation is not just about keeping up with the competition; it’s about positioning your business for long-term success in a rapidly changing marketplace.
I don’t think the title of your article matches the content lol. Just kidding, mainly because I had some doubts after reading the article.