If you recently had a urine test and noticed the abbreviation “ket” on your lab results, you might be wondering what it means. In medical testing, “ket” refers to ketones, which are chemicals produced when your body burns fat for energy instead of glucose. A urine test can detect ketones and provide insights into your metabolism, diet, and overall health.
Understanding what ket means on a urine test is crucial, whether you’re monitoring diabetes, following a ketogenic diet, or undergoing a routine medical check-up. In this guide, we’ll break down the meaning of ketones in urine, potential causes, health risks, treatment options, and FAQs—all backed by medical sources and practical insights.
What Does “Ket” Mean on a Urine Test?
On a standard urine test (urinalysis), “ket” or “ketones” refers to the presence of ketone bodies. These are substances produced when your body breaks down fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.
There are three main types of ketones detected in urine:
- Acetoacetate
- Beta-hydroxybutyrate
- Acetone
Normally, ketone levels in urine are very low or undetectable. However, under certain conditions—such as fasting, low-carb diets, or uncontrolled diabetes—ketone levels can rise significantly.
In short: If your urine test shows “ket,” it means your body is in a state of ketosis or possibly experiencing a medical issue related to fat metabolism.
Why Do Doctors Test for Ketones?
Doctors order urine ketone tests to monitor conditions such as:
- Diabetes management (especially type 1 diabetes)
- Unexplained weight loss or malnutrition
- Pregnancy-related complications like gestational diabetes
- Low-carbohydrate diets (keto diet followers often test for ketones)
- Metabolic or digestive disorders
This test helps determine whether the body is using fat instead of glucose for fuel, which can be healthy in some cases (like dieting) or dangerous in others (like diabetic ketoacidosis).
Causes of Ketones in Urine
Ketones in urine can appear due to various reasons, ranging from lifestyle factors to serious health conditions.
1. Dietary Causes
- Low-carb or ketogenic diet
- Prolonged fasting
- Skipping meals frequently
2. Medical Conditions
- Diabetes (Type 1 & Type 2) – especially uncontrolled
- Gestational diabetes during pregnancy
- Hyperthyroidism (overactive thyroid)
- Alcohol use disorder
3. Other Causes
- Severe dehydration
- Strenuous exercise
- Eating disorders like anorexia
Ketones in Urine Levels Chart
Here’s a simplified chart of how ketone levels are usually interpreted:
| Ketone Level (mg/dL) | Urine Test Result | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Negative (0 mg/dL) | Normal | No ketones detected |
| Trace (5–20 mg/dL) | Mild ketosis | Could be due to diet/fasting |
| Moderate (20–50 mg/dL) | Moderate ketosis | May indicate poor diabetes control |
| High (>80 mg/dL) | Severe ketosis | Possible diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) |
Important: High levels of ketones in urine require immediate medical attention, especially for people with diabetes.
Ketones in Urine and Diabetes
One of the most important reasons doctors check for ketones is to monitor diabetes complications.
Diabetic Ketoacidosis (DKA)
When insulin levels are too low, glucose cannot enter cells for energy. As a result, the body starts burning fat, producing excessive ketones. This condition is called diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA), which can be life-threatening.
Symptoms of DKA include:
- Extreme thirst and frequent urination
- Nausea and vomiting
- Confusion or difficulty concentrating
- Fruity-smelling breath
- Rapid breathing
If you have diabetes and your urine test shows high ketones, seek medical help immediately.
Ketones in Urine During Pregnancy
Ketones can sometimes be detected in the urine of pregnant women. Common causes include:
- Morning sickness (leading to dehydration)
- Gestational diabetes
- Poor dietary intake due to nausea or loss of appetite
While mild ketones are often harmless, moderate to high levels during pregnancy should be checked by a healthcare provider.
Ketones and the Ketogenic Diet
For people intentionally following a keto diet, the presence of ketones in urine is often a positive sign. It indicates that the body has entered nutritional ketosis, burning fat instead of carbs.
However, the levels are usually mild to moderate—not dangerously high like in DKA.
Keto dieters use urine ketone strips to track progress. These strips are affordable and widely available at pharmacies.
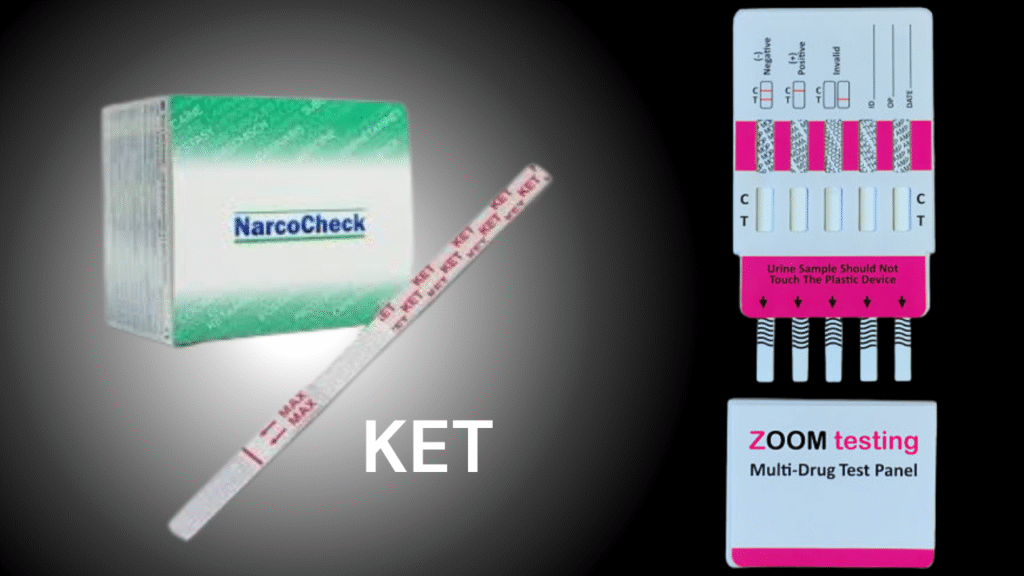
How Are Ketones in Urine Detected?
Urine ketones can be tested in two main ways:
- Dipstick Test (Home Use)
- Affordable and easy to use
- Results appear within minutes
- Colors on the strip indicate ketone levels
- Laboratory Urinalysis
- More accurate than home tests
- Often part of routine medical exams
- Provides detailed results for doctors to interpret
How to Reduce High Ketones in Urine
If your urine test shows elevated ketones, here are steps you can take:
- For people with diabetes:
- Check your blood sugar frequently
- Take insulin as prescribed
- Stay hydrated with water or electrolyte drinks
- For non-diabetics:
- Eat balanced meals with sufficient carbs
- Avoid excessive fasting or starvation
- Limit alcohol consumption
- Rest after intense exercise
Always consult a healthcare provider before making major dietary or medication changes.
Risks of Ignoring High Ketone Levels
Leaving high ketone levels untreated can lead to serious complications:
- Diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA) – life-threatening condition
- Electrolyte imbalance
- Organ damage (kidneys, liver)
- Coma in severe cases
When to See a Doctor
Seek medical help if you notice:
- Persistently high urine ketone readings
- Symptoms of DKA (nausea, vomiting, fruity breath, confusion)
- Pregnancy with moderate or high ketones
- High blood sugar combined with ketones
FAQs About Ketones in Urine
1. What does ket mean on a urine test?
It means ketones are present in your urine, which happens when your body burns fat for fuel instead of glucose.
2. Are ketones in urine always dangerous?
No. Mild ketones can occur due to diet or fasting. But high ketones, especially in people with diabetes, can be dangerous.
3. Can dehydration cause ketones in urine?
Yes. Dehydration reduces glucose availability, forcing the body to burn fat and produce ketones.
4. What’s the difference between ketosis and ketoacidosis?
- Ketosis is a natural, controlled state (e.g., keto diet).
- Ketoacidosis is a dangerous medical emergency (seen in diabetes).
5. How do I test for ketones at home?
Use over-the-counter urine ketone strips. They are affordable and give quick results.
Explore More Articles
9202823875 Phone Number Explained – Scam or Legit?”
HP P224 Monitor Review: Specs, Features, Price & Use Cases
Suhaib Zaino: The Digital Visionary Shaping Modern Online Media
George Zajfen Autopsy: Full Report and Key Findings Explained
Fabiola Kramsky: Biography, Background & Public Profile
Glynn Daly: A Full Biography, Legacy & Influence
Conclusion
So, what does ket mean on a urine test? In simple terms, it indicates the presence of ketones, substances your body produces when burning fat for energy. While small amounts may be normal (especially for keto dieters or during fasting), moderate to high levels can signal health concerns such as diabetes complications, dehydration, or pregnancy-related issues.